Remember the days of standing on the street, desperately hoping a taxi would stop? Uber changed all that, revolutionising the way we travel. Today, booking a ride is as simple as tapping your phone.
But have you ever thought about how Uber actually makes money? It started as a simple taxi booking service, but over time, it has grown into a global ride-hailing business offering much more than just cab rides. Today, Uber offers services like freight transportation, luxury rides with Uber Black, and food delivery through Uber Eats.
In this article, we’ll explore how Uber started, its funding journey, the challenges it faces, how it earns revenue, and its key competitors.
Overview Of The Uber Business Model
| Point | Overview |
| Company Name | Uber |
| Founded | 2009 |
| Founders | Garrett Camp & Travis Kalanick |
| Headquarters | San Francisco, California, USA |
| Industry | Ride-Hailing, Mobility & Logistics |
| Available | 70+ Countries |
| Cites | 15,000+ cites |
| Monthly Active Users | 189M+ users |
| Drivers and Couriers | 9M+ |
| Business Model | Aggregator-based ride-hailing platform |
| Key Services | Ride-Hailing, Uber Eats, Uber Freight, Rentals, Premium & Shared Rides |
| Gross Bookings | $49.7 Billion |
| Revenue (2024) | $43.9 Billion |
How Uber Started?
There are two quick stories about the Uber ideation stage,
One is when Garrett Camp, the co-founder of Uber, came from a New Year’s party with his friend in 2008, and they had to pay $800 to a private driver. He thought, if there was any way to share this ride with 1-2 more persons, the cost of the ride would be reduced.
Another popular story was when Travis Kalanick and Garrett Camp attended the conference in Paris in 2008. On returning to their home, they struggled to find a taxi for so long, and this inconvenience inspired them to create a taxi booking app named “UBER”.

In 2010, both of them launched Ubercabs.com as a beta version. And in mid 2010, they finally launched Uber services in San Francisco. It was the first app at that time to book rides directly from smartphones. And very soon, they started getting a lot of popularity.
And at that time, anyone can become a driver with Uber Cabs. And then they got legal notices on behalf of private taxi services. After all the legal hassle, they changed their brand name from Ubercabs.com to Uber.com, and so far, Uber is ruling the taxi booking market.

Global Expansions Of Uber
Uber started its expansion in 2013 in India because of India’s massive population and demand for affordable transportation.
In the same year, they also expanded to China because of its immense potential and to compete with China’s local competitor, Didi Chuxing. But by August 2016, Uber China’s business merged with Didi Chuxing. This merger happened because of the influence of its major investor, Softbank.
In Southeast Asia, Uber faced stiff competition from Grab and Go-Jek, leading to strategic adaptations. In 2018, Uber sold its Southeast Asian operations to Grab in exchange for a stake in the company, marking another significant consolidation in its expansion strategy.
From those learnings, Uber started adapting to the local market trends. It introduced various unique services to meet region-to-region needs. In India, Uber rolled out cash payments and auto-rickshaw rides to cater to a broader audience.
Similarly, in Thailand, Uber introduced a motorbike service to cater to Thailand’s congested cities.
Despite all the ups and downs, Uber remains one of the most innovative and influential companies in the transportation industry, consistently expanding its reach to more developing and developed nations.
Funding Rounds Of Uber
Uber has raised a total of $13.2 billion across 26 funding rounds. The company’s biggest funding came in June 2016, when Uber raised $3.5 billion in its Series G round, led by the Public Investment Fund.
Below is the list of Uber’s funding rounds:
| Year | Funding Round | Amount Raised | Investors |
| August, 2009 | Angel | 200K | Lance Michael Comes |
| October 15, 2010 | Seed | $1.25M | First Round Capital and other investors |
| February 14, 2011 | Series A | $11 million | Benchmark and other investors |
| September 12, 2012 | Series B | $37.3M | Menlo Ventures, Benchmark, Goldman Sachs and others |
| August 14, 2013 | Series C | $361M | Google Ventures, TPG and more |
| June 6, 2014 | Series D | $1.2B | Fidelity Investments, Wellington, BlackRock, Summit Partners |
| December 4, 2014 | Series E | $2.8B | Sequoia Capital, TPG, New Enterprise Associates, Qatar Investment Authority, Lone Pine Capital, Valiant Capital Management and more |
| January 22, 2015 | Conventional Debt | $1.6B | Goldman Sachs |
| March 23, 2015 | Series E | – | Times Internet, Lauder Partners |
| May 12, 2015 | Series E | $1.69B | Goldman Sachs Investment Partner |
| 2015 | Series E | – | IVP |
| 2015 | Series E | – | Alive Partners, FJ Labs |
| July 31, 2015 | Series F | $1B | Microsoft, Kingdom Holding Company |
| August 19, 2015 | Series F | $75M | Tata Opportunities Fund |
| February 12, 2016 | Series F | $200M | LetterOne |
| May 24, 2016 | Series F | – | Toyota |
| June 2, 2016 | Series G | $3.5 billion | Public Investment Fund |
| July 7, 2016 | Series G | – | Fort Ross Ventures |
| September 23, 2016 | Series G | $30M | Kumpulan Wang Persaraan |
| January 18, 2018 | Series G | $1.3B | Softbank Vision Fund and more |
| March 23, 2018 | Conventional debt | $1.5B | – |
| August 28, 2018 | Series G | $500M | Toyota |
| April 26, 2019 | Series G | $500M | Paypal |
| September 13, 2019 | Conventional debt | $1.2B | Wall Street, Public Investors |
| December 19, 2020 | Post IPO | $1.15B | Public |
Acquisitions & Mergers Of Uber
| Year | Company | Type Of Company | Acquisition Amount |
| March 2015 | deCarta | Mapping Startup | – |
| August, 2016 | Otto | Self-driving truck company | $680M |
December, 2016 | Geometric Intelligence | AI startup | – |
| July, 2017 | Swipe Labs | Social product studio | — |
| July, 2017 | Complex Polygon | Product studio that builds and launches mobile applications | – |
| April, 2018 | Jump Bike | A startup that offers pedal-assist electric bikes | $200M |
| March, 2019 | Careem | Ride-hailing company | $3.1B |
| June, 2019 | Mighty AI | a startup that specialises in building training data for computer vision. | – |
| October, 2019 | Cornershop | Online grocery provider | – |
| July, 2020 | Routematch software | Turkish Food Delivery Platform | – |
| August, 2020 | Autocab | Taxi technology company | – |
| December, 2020 | Postmates | American food delivery service | $2.65B |
| Feb, 2021 | Drizly | Alcohol delivery service | $1.1B |
| July, 2021 | Transplace | leading provider of advanced logistics technology and solutions | $2.25B |
| August, 2021 | HK Taxi | Local taxi hiring app in HongKong | – |
| January, 2022 | Car Next Door | Australian car-sharing company | – |
| December, 2024 | Foodpanda | Online food delivery and ordering platform | – |
| May, 2025 | Trendyol Go | Turkish Food Delivery platform | $700M |
| May, 2025 | Dantaxi | Denmark’s taxi company | – |
| June, 2025 | Crowntaxi | Taiwan local taxi company | – |
How Uber Works?
To use Uber’s ride-hailing service, you need a smartphone with GPS, internet access, and the Uber app.
- Open the Uber app and sign up using your phone number.
- Enter your pickup location and destination.
- You’ll see a list of different vehicle options like Uber Auto, Uber Bike, Uber Go, etc., along with the price for each. Choose the vehicle that suits you best.
- The app finds a nearby available driver based on your location and the driver’s location.
- Once the driver arrives, you share the OTP to verify your ride.
- Your fare is calculated automatically based on distance, time taken, and current demand.
- You can see the estimated fare in the app before or after the ride, depending on the service.
Note: The price changes depending on the type of vehicle you select.
Products and Services offered by Uber:
1. Drive with Uber (Uber Taxi):
Drive with Uber is one of the most popular and first offerings from Uber that allows drivers and fleet owners to sign up as drivers and start their taxi business with them. As a driver, they can choose their working hours or how often they want to drive per day/week.
2. UberEats
Uber Eats is an online food delivery service launched by Uber in 2014. People can order food from nearby restaurants through the Uber Eats app (just like Swiggy in India). The food gets delivered by their delivery partners.
3. Uber for Businesses
Uber for Business is a platform for corporate companies and startups to manage rides, meals, and deliveries for their employees. Launched in 2014, it allows businesses to create a central Uber account that employees can link to their own Uber accounts.
Instead of paying for uber rides or meals themselves, employees can charge expenses directly to the company account—making it easier to track spending and manage budgets.
4. Uber Freight
Uber Freight is a logistics and transportation service launched in 2017. This platform helps to send bulky items from one place to another hassle-free.
5. Uber X
Uber X is a budget-friendly taxi service launched in 2012. It provides high-quality and reliable rides in four-door sedans.
6. UberX Share
UberX Share is basically the rebranded version of Uber Pool, sometimes called Group Rides. It lets you share your ride with other people going in the same direction, so you pay less. It’s a budget-friendly carpool option with added safety features.
And, in some regions, riders can even earn small cash incentives for sharing.
7. Uber Electric (Earlier Uber Green)
Uber Green is now called Uber Electric. This option lets you book fully EV/hybrid car for zero-emission rides. It’s meant for people who want a more sustainable travel choice while reducing carbon emissions.
In India, Uber Electric is available in select cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Bengaluru.
8. Uber Rentals
Uber rental allows you to rent a taxi, launched in June 2020 amidst the pandemic. It allows passengers to rent a car with a driver for multiple stops and a set amount of time—from 1 to 12 hours.
9. UberXL
Uber XL is another kind of taxi service for a group of people, launched in 2015. With this, you can book bigger cars and SUVs for a group of people.
10. Uber Comfort
Uber Comfort offers newer vehicles with extra legroom and experienced, highly rated drivers. It’s best when you want a more relaxed, comfortable ride without the luxury price tag.
11. Uber Black
Uber Black is a premium ride service that offers luxury cars like BMW, Mercedes-Benz and others with premium customer support service.
12. Uber Shuttle
Uber Shuttle is a budget-friendly option that lets you share rides in buses and vans, making it easier and cheaper to get to and from places.
It’s currently active in some regions like Delhi-NCR and Kolkata (India) and Cairo (Egypt).
13. Uber intercity
Uber Intercity allows you to book long-distance, outstation rides directly through the Uber app, so that you can travel from one city to another for work, trips, or family visits. It offers features like one-way trips, multi-day round trips, advance booking, and door-to-door service for comfort and convenience.
14. Uber WAV
Uber WAV stands for Wheelchair Accessible Vehicle. This service is for riders who use wheelchairs, including non-folding ones. These vehicles come with ramps or lifts and trained drivers, ensuring safe and comfortable travel.
Business Model of Uber
The Uber Business model is simple yet powerful. It works as an aggregator platform, connecting people who need a ride with the drivers who provide the service.
It primarily charges a flexible charge of 15% to 25% (ride commissions) of the total ride amount from the drivers. In that percentage, Uber provides them with passengers, helps with navigation, and ensures they can earn flexibly – all while focusing on safety and timely rides as per their convenience.
Apart from this aggregator model, it’s trying a couple of more ways to make money, as below,
How does Uber earn money?
Here’s a breakdown of how Uber earns:
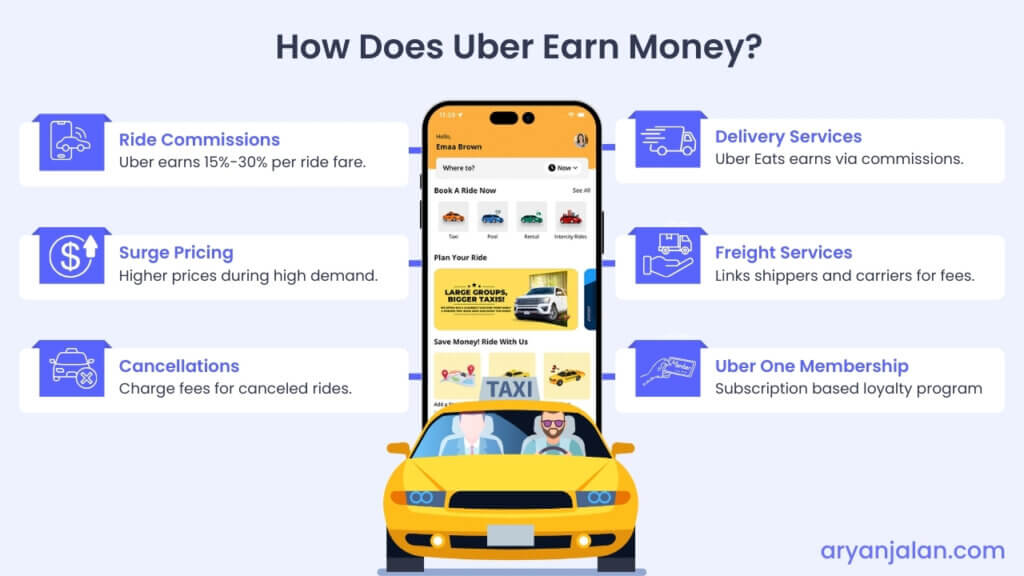
1. Ride Commissions:
Uber makes money by taking a commission on every ride. When a customer hires an Uber cab, Uber gets 15% to 30% of the fare, and the rest goes to the driver.
2. Surge Pricing:
Uber also makes some money with Surge pricing. During busy times (like rush hour), Uber increases prices to meet high demand. This helps both Uber and the drivers earn more money because customers pay more, and drivers get higher fares.
Definition: Surge Pricing is a pricing algorithm that adjusts based on demand, thus increasing revenue.
3. Cancellations:
This is another way for Uber to make money from the rider’s side. If a rider cancels a ride after booking, Uber charges a cancellation fee. The closer the cancellation is to the ride time, the higher the fee.
Other revenue streams of Uber
1. Delivery Services (UberEats):
Uber Eats operates in over 11,500 cities across 45 countries, but its services are unavailable in India. However, it’s a big player in the food delivery app globally and generates revenue through multiple streams.
Just like any other food delivery platform, Uber charges restaurants a commission of 15-30% from every order placed through its app. It also charges delivery fees, and cancellation fees from the users.
And also generates revenue through advertising and marketing fees from restaurants to promote their deals on the UberEats app.
2. Freight Services:
Uber Freight is another way Uber makes money. It offers freight services and currently operates in many global markets.It connects shippers (people who need to send goods) with carriers (truck drivers). It earns money by charging for each shipment booked through its app, offering transparent pricing to shippers and carriers.
3. Uber One (membership program)
Uber makes money from its Uber One subscription by encouraging users to spend more. With discounts and benefits, it attracts frequent users, making them use Uber more often.
This subscription service is already popular in countries like the US (launched in 2021) and Canada. And recently in India.
Strategic Partnerships of Uber
Some recent strategic partnerships of Uber:
1)- Uber has partnered with Baidu to start robotaxi testing in the UK, with trials planned to begin in the first half of 2026.
2)- In November 2025, Uber launched driverless robotaxis in Abu Dhabi in partnership with WeRide, marking a major step toward self-driving ride services in the region.
3)- Uber has joined forces with Avride, a U.S.-based autonomous vehicle startup, to bring delivery robots and self-driving vehicles to its services.
4)- In October 2024, Uberteamed up with the Indian Air Force (IAF) to offer transportation solutions for official travel and daily commutes for personnel and their families.
5)- Uber has partnered with logistics provider Shadowfax to expand its two-wheeler taxi service, UberMoto, by integrating Shadowfax’s bike fleet.
6)- During the 2020 lockdown, Uber launched a last-mile delivery service and partnered with Bigbasket to deliver groceries and essentials to customers’ homes in India.
7)- Back in 2018, Uber partnered with Toronto-based Autzu, enabling Uber drivers to rent electric Teslas by the hour.
Uber Competitors
1)- Ola Cabs – Primary in India
2)- Lyft – In the United States
3)- Grab – In South East Asia
4)-Go-Jek – In South East Asia
5)- Curb – In the United States
Some Interesting Facts About Uber
1)- Uber is the world’s largest ridesharing company, with over 189 million monthly users and 9 million drivers and couriers.
2) Uber generated $43.9 billion in revenue in 2024, which was an 18% increase compared to the previous year.
3)- Uber completed 11.2 billion trips in 2024 across its platform.
4)- In Q3 of 2025, Uber recorded $49.7 billion in gross bookings worldwide.
5)- In Q2 2025 alone, users completed 3.27 billion trips through Uber.
6)- As of March 2024, Uber held a 76% share of the US ride-hailing market, making it the clear market leader.7)- As of 2025, Uber operates in over 15,000 cities (across 70 countries) and serves more than 700 airports worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions Of Uber
1)- How does the Uber Business model work?
It connects riders with drivers through an app and takes a cut from each ride.
2)- How much do Uber drivers make?
It depends, but drivers generally earn $15–$25 per hour, based on location and demand.
3)- What is Uber one?
It’s a subscription service with discounts on rides and Uber Eats orders.
4)- How does Uber work?
You book a ride on the app, and a nearby driver picks you up and drops you off.
5)- When did Uber start?
Uber launched its services in 2010.
6)- When was Uber founded?
Uber was founded in March 2009.
7)- Who is the founder of Uber?
Garrett Camp and Travis Kalanick started Uber.
8)- How does Uber generate revenue?
Mainly through ride commissions, surge pricing, delivery fees, and memberships like Uber One.
Read More About:
1. WhatsApp Business Model
2. Lenskart Business Model
3. Cars24 Business Model
4. Khatabook Business Model
5. Paytm Business Model


